Platform Ingress
Platform Ingress
Platform Ingress is responsible for creating the Ingress setup.
Design
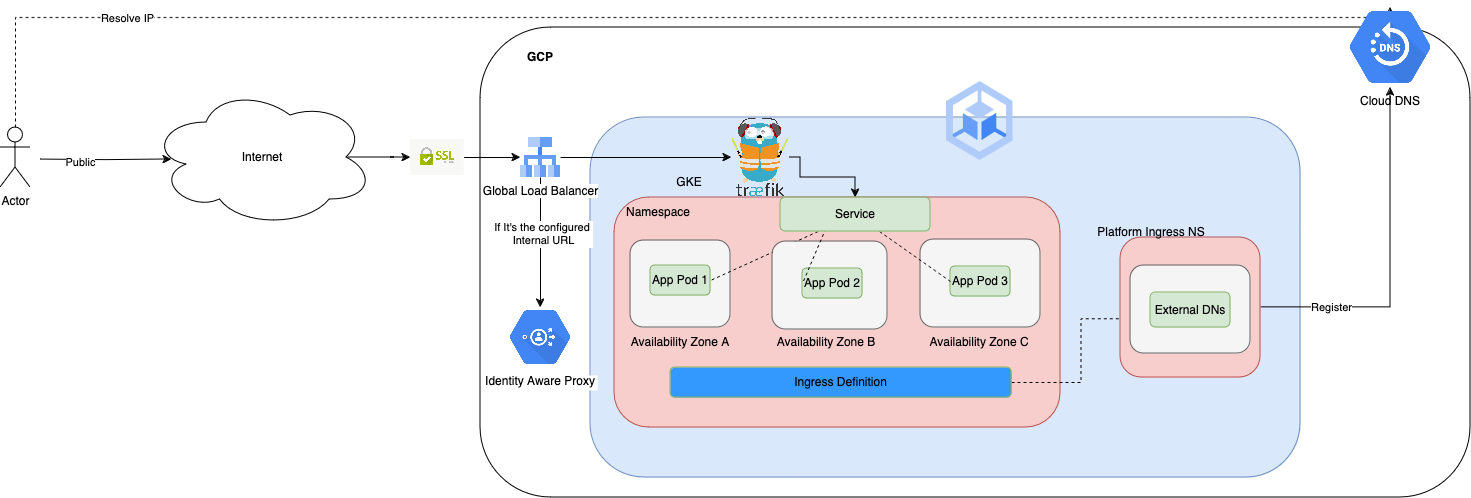
Ingress design
What does it include?
- Public and Private access
- Cloud DNS managed zones to manage the DNS
- External DNS
- Traefik Ingress controller
How does DNS work?
Out of the box we will provide a subdomain of cecg.io. If they have their own domain, that can be configured based on the config.yaml. The base construction will be:
<environment>.<organization>.<ingressDomain>, for example, sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io. The private URL construction will be configurable on the environment config file, but we typically keep the same one with an internal suffix, like sandbox-gcp-internal.cecg.cecg.io
The platform-ingress module install a Gateway object that creates a GCP load balancer. External DNS picks that up and registers them with A records with the LB IP. All other domains are registered as CNAME records pointing to the A records.
If they use our cecg.io domain, there is an additional step that needs to be done for DNS Delegation. Since we own the domain, when trying to resolve anytihing ‘*.cecg.io` it will hit our DNS managed zones. We can however delegate the resolution of certain subdomains to specific. See DNS.
DNS delegation
How can clients manage records on a subdomain they do not own? We need to create a DNS delegation.
For cecg for example, we’ll need to delegate that subdomain to cecg client.
To do that, all you need to do is to create a NS record with the nameservers on the managed zone the cecg client created.
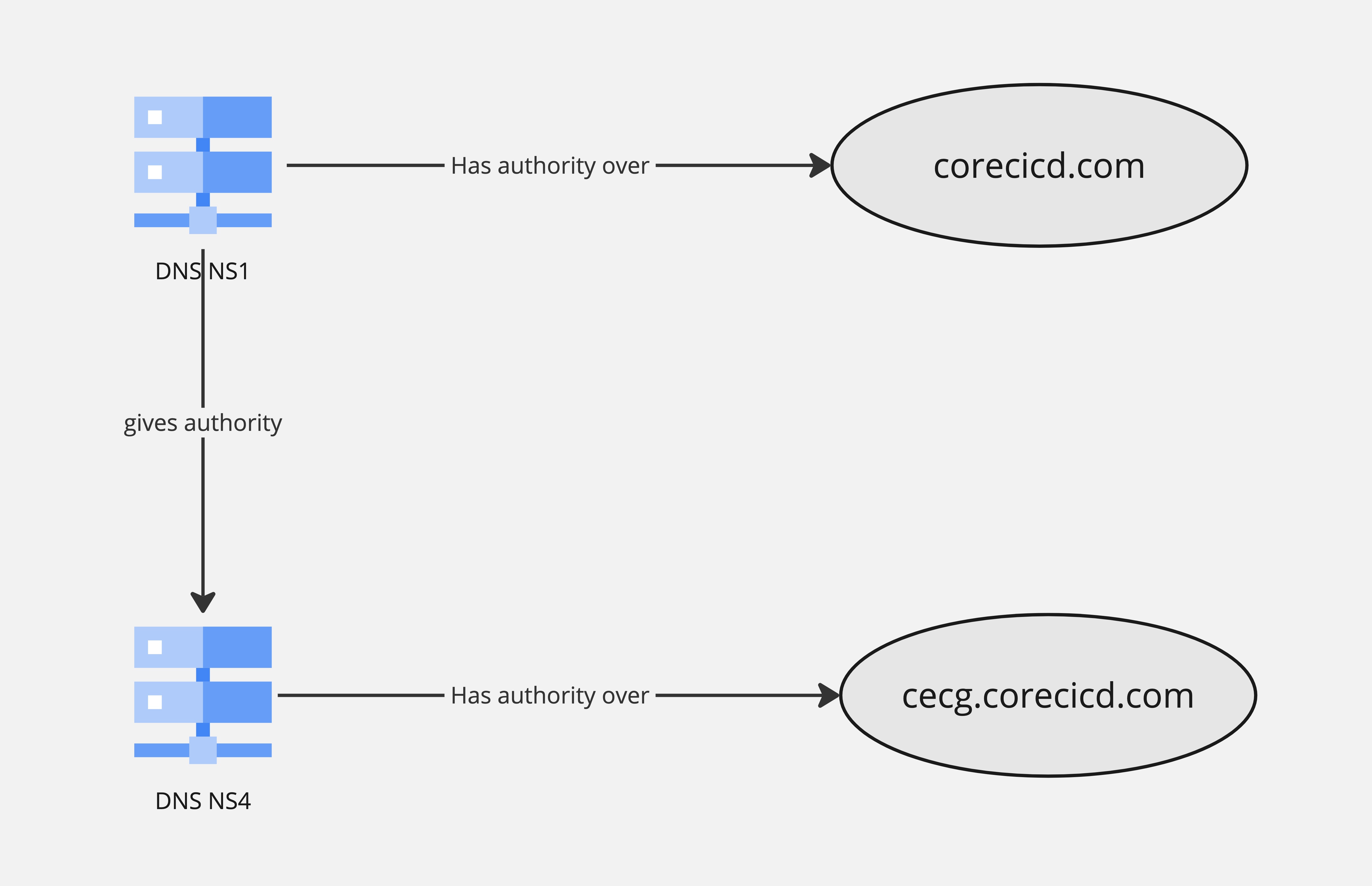
DNS Delegation
How can I differentiate between internal and external
There is a single ingress controller and load balancer. The way to differentiate is to use the ingress you configure in the environments config.yaml as internalService, for example sandbox-gcp-internal.cecg.cecg.io. Anything that hits that URL will be forward to the IAP for authentication and validations. Only people in the platform-readonly@<domain> google groups will be able to access that URL.
This means that everything is public because we do not use VPNs to access the cluster and always go through a public LB, but we can restrict the access using IAP.
For external DNS to work, each ingress will need to have the annotations
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: reference-app.sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target: sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.ioSSL
This will work out of the box until the LB using Let’s Encrypt. It uses a single level certificate (eg. *.sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io) which will allow users to create single level subdomain like learn-functional.sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io. Any more levels won’t work unfortunately.
Example ingress
External Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: reference-app-external
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: reference-app.sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target: sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io
namespace: golang-dev
spec:
ingressClassName: platform-ingress
rules:
- host: reference-app.sandbox-gcp.cecg.cecg.io
http:
paths:
- path: /hello
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: reference-service
port:
number: 80Internal Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: grafana
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: reference-app.sandbox-gcp-internal.cecg.cecg.io
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target: sandbox-gcp-internal.cecg.cecg.io
namespace: platform-monitoring
spec:
ingressClassName: platform-ingress
rules:
- host: reference-app.sandbox-gcp-internal.cecg.cecg.io
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: platform-grafana-service
port:
number: 3000For more information on how to use this, please look at the App Ingress section.
Autoscaling
Platform Ingress scales automatically based on resource consumption to handle spikes of traffic.
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling is enabled for Traefik pods and is configurable via config.yaml.
The following example overrides resource requests for Traefik pods, sets a range for the number of replicas and overrides the CPU usage percentage threshold.
platformIngress:
resources:
requests:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "300Mi"
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 21
cpuPercent: 80Future work
We aim to be tech agnostic and remove some redundancies, namely regarding external-dns annotations. For that we will create a mutating webhook that will inject the needed annotations based on the URL of the ingress. It will also check for conflicts in the configuration and block the creation of any already existing as that will cause the IC to load balance between 2 possibly completely distinct application